Solução Perfeita para obtenção de resultados únicos – O seu projeto nunca esteve em melhores mãos!

-
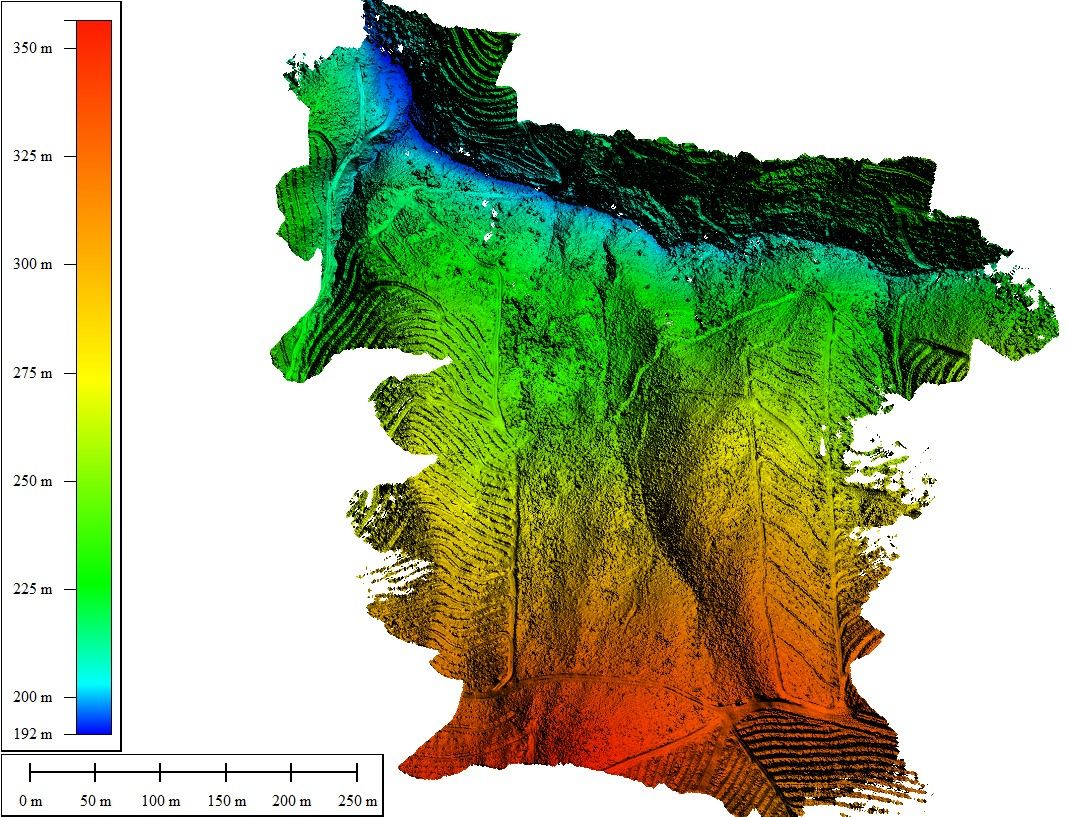
Point Cloud
-
Digital Elevation Model (DEM)
-
Intensity
-
Classification
-
Color Information
Core Data
- Point Cloud: This is the raw data, consisting of millions of individual points reflecting the laser pulses. Each point has an X, Y, and Z coordinate representing its location in space.
- Digital Elevation Model (DEM): This is a surface model representing the bare earth elevation by removing vegetation and structures from the point cloud. DEMs are invaluable for topographic mapping, flood modeling, and terrain analysis.
- Digital Surface Model (DSM): This model includes all above-ground features like buildings, vegetation, and power lines. It’s useful for infrastructure management, 3D city models, and visibility simulations.
Additional Data
- Intensity: Reflects the strength of the returned laser pulse, indicating surface properties like material and reflectivity.
- Classification: Categorizes points based on their type (ground, vegetation, building, etc.), aiding in data analysis and interpretation.
- Color Information: LiDAR data can be combined with RGB imagery collected simultaneously, adding color information to each point.
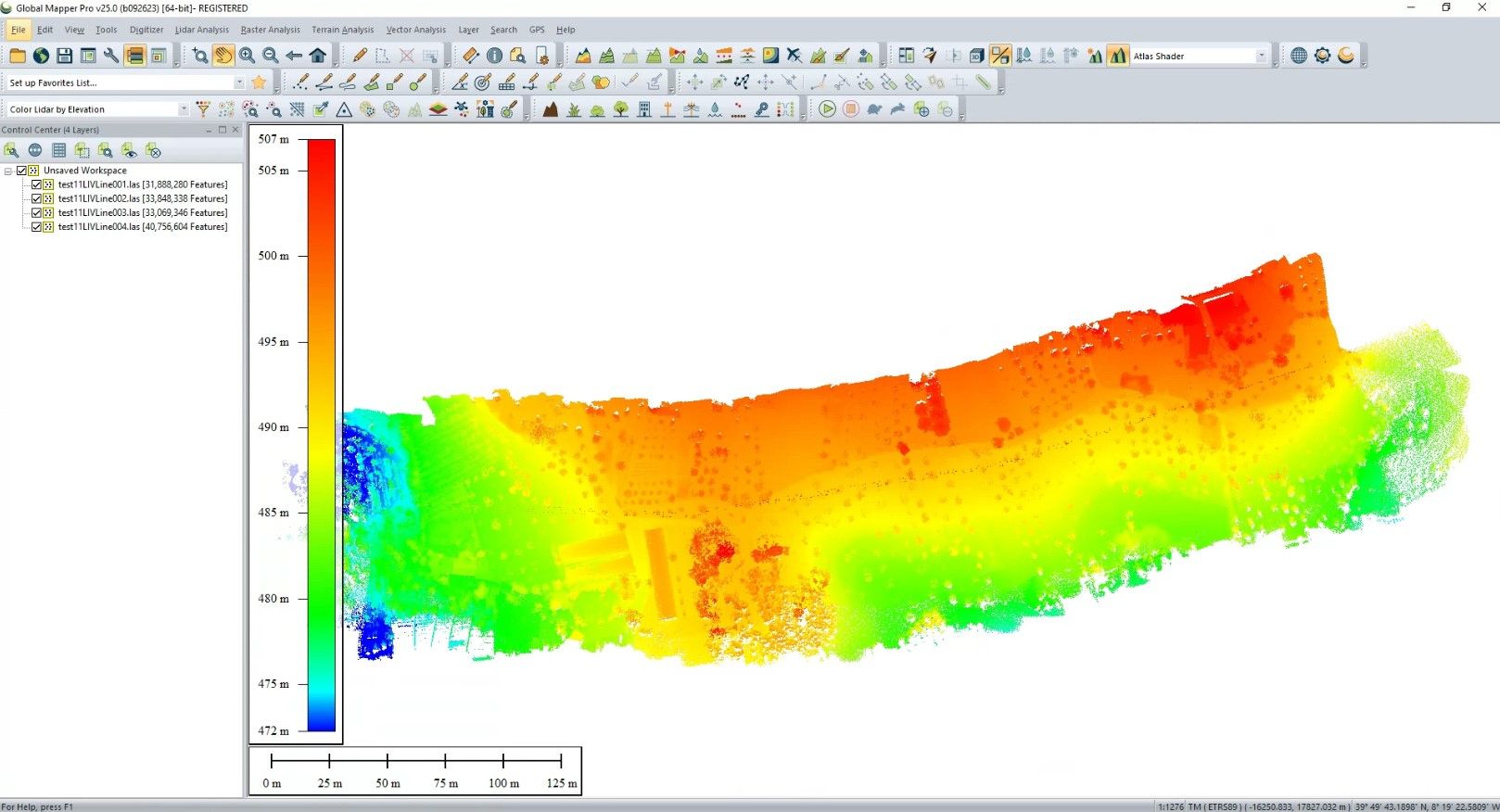
Corridor Lidar Point Cloud (Geosun GS-100C+ and Global Mapper)
Benefits of drone lidar data
Drones can cover large areas quickly and efficiently, reducing overall project time and labor costs compared to ground-based surveys.
Drones can navigate complex terrains and reach areas inaccessible to traditional methods, eliminating expensive scaffolding or manual surveying in hazardous environments.
Smaller crews and less equipment are needed with drone LiDAR, leading to lower logistical costs and faster deployment.
Drone LiDAR captures millions of data points per square meter, leading to highly detailed and accurate 3D representations of the target area.
Drones can achieve centimeter-level accuracy, crucial for applications like construction, mapping, and infrastructure inspection.
LiDAR can see through vegetation cover, revealing the underlying terrain, valuable for forestry, flood modeling, and archaeological surveys.